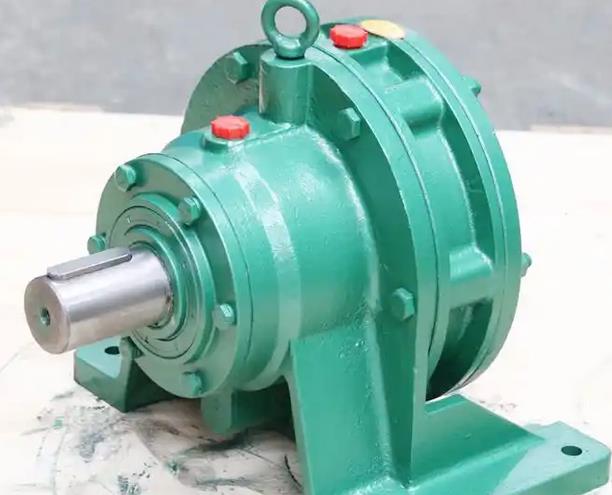
What factors can affect the normal operation of the CFD200 cooling tower fan reducer?
The following factors will affect the normal operation of the CFD200 cooling tower fan reducer:1. Lubrication issues
Lack of lubrication: If the lubricating oil or grease in the reducer is insufficient, the friction of components such as gears and bearings will increase, leading to overheating and wear, affecting normal operation.
Oil contamination: Lubricating oil is contaminated by dust, moisture, metal particles, etc., which reduces the lubrication effect and increases the risk of wear.
Oil aging: Lubricating oil used for a long time will age and become ineffective, losing its lubrication and protective effects.
2. Load situation
Overloading: The cooling tower fan is overloaded beyond the design range, and the deceleration machine may accelerate wear and even damage due to overload.
Frequent start stop: Frequent start and stop generate impact loads, increasing fatigue damage to mechanical components.
3. Installation aspect
Misalignment: Misalignment between the reducer and the motor or other connecting components can intensify vibration and wear mechanical parts.
Unstable foundation: The cooling tower foundation is unstable or not installed firmly, causing vibration during system operation and affecting the operation of the gearbox.
4. Environmental factors
High temperature: High temperature reduces the performance of lubricating oil, accelerates the aging and wear of mechanical components.
High humidity: High humidity environments can easily cause rusting inside the gearbox. For gearboxes that are not well sealed, moisture entering can cause corrosion.
Dust pollution: Dust and pollutants in the air enter the gearbox, affecting operation and exacerbating wear.
5. Maintenance and upkeep
Missing inspection: Failure to regularly inspect and maintain as required by the manufacturer, making it difficult to detect potential issues in a timely manner.
Inadequate cleaning: Failure to clean the surroundings and equipment of the cooling tower for a long time leads to the accumulation of dust and debris, which affects heat dissipation and normal operation.
6. Manufacturing defects
Material issue: Gearboxes made of inferior materials have poor strength and wear resistance, and are prone to malfunctions.
Process defects: Improper assembly, insufficient machining accuracy, and other process defects during production can affect the service life.
7. Electrical malfunction
Voltage fluctuation: The unstable voltage of the power grid leads to fluctuations in the output power of the motor, causing additional stress on the gearbox.
Component aging: The aging or damage of electrical components in the control system may cause the motor to lose control and damage the gearbox.
8. Vibration issue
Unbalanced load: Unbalanced fan blades or misaligned fan shaft can cause excessive vibration, affecting the lifespan of the gearbox.
Resonance phenomenon: Vibration at certain frequencies causes resonance, amplifying the amplitude of the vibration and exacerbating the wear of mechanical components.



