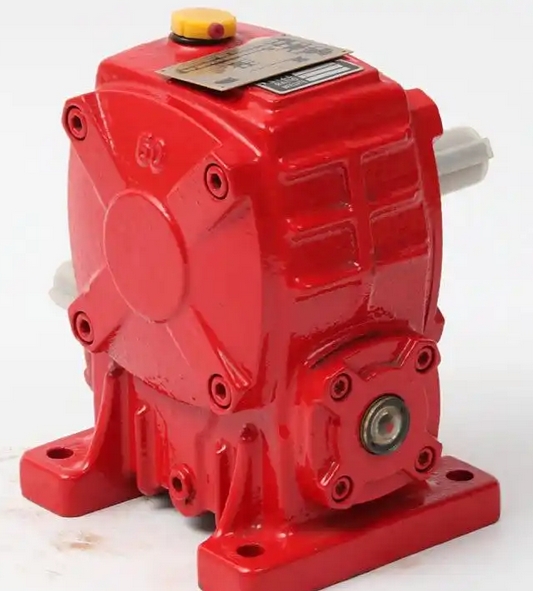
What are the differences between ordinary worm gear transmission and self-locking worm gear transmission
The difference between ordinary worm gear transmission and self-locking worm gear transmission is as follows:1. Self-locking property
Ordinary worm gear transmission usually does not have self-locking function, while self-locking worm gear transmission can achieve reverse self-locking (i.e. the worm wheel cannot drive the worm) when the worm lead angle is less than the equivalent friction angle of the meshing surface. This feature makes self-locking transmission suitable for scenarios such as lifting machinery and lifting devices that require anti reversal measures.
2. Transmission efficiency
The efficiency of ordinary worm gear transmission is generally 70% -90%, while the efficiency of self-locking transmission is even lower (usually less than 50%), mainly due to greater friction losses. The efficiency difference is due to the smaller helix angle of the worm gear in self-locking transmission, which leads to increased sliding friction.
3. Structural design
The number of worm heads in self-locking worm gear transmission is usually single (Z1=1) to increase the transmission ratio and reduce the lead angle, while ordinary transmission may use multi head worm (Z1=2-4) to improve efficiency. In addition, self-locking worm gears often use wear-resistant bronze materials to cope with higher friction.
4. Application scenarios
Ordinary transmission is suitable for applications that require high efficiency, such as machine tools and automobiles, while self-locking transmission is often used for equipment with strict safety protection requirements, such as elevators and lifting machinery.
5. Heating and maintenance
Self locking transmission requires more frequent lubrication and heat dissipation measures due to low efficiency, high friction, and more severe heating. The maintenance cost of ordinary transmission is relatively low.



